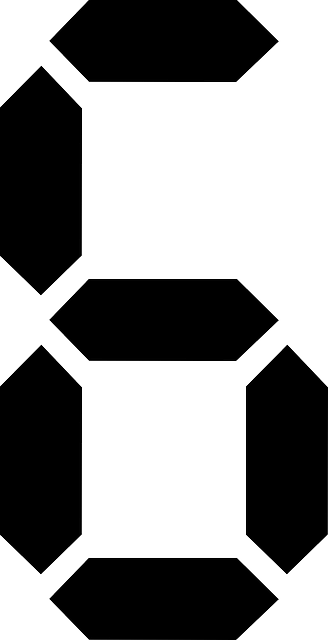
Discover the transformative power of Lean Six Sigma, a proven methodology for process improvement. This guide outlines its key principles and real-world applications, highlighting the significance of the Six Sigma Certification. It demonstrates how Six Sigma Black Belt professionals lead organizations through the DMAIC phase, defining clear goals and identifying problem areas to enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and drive exceptional quality. The text emphasizes that six sigma training equips employees with tools to break down complex issues, ensuring successful initiatives and verifying expertise through certification.
- Understanding Six Sigma: Unveiling the DMAIC Process
- Define: Setting Clear Goals and Establishing Metrics
- Measure: Data Collection and Performance Analysis
- Improve & Control: Implementing Changes and Sustaining Results
Understanding Six Sigma: Unveiling the DMAIC Process

Define: Setting Clear Goals and Establishing Metrics

In the Define phase of the DMAIC process, organizations set clear and measurable goals that align with their overall strategic objectives. This step is pivotal in six sigma and lean six sigma methodologies, as it establishes a foundation for successful project execution. By defining the problem or opportunity, you identify what needs improvement and set specific targets to achieve significant results. Key to this phase is establishing metrics, which provide quantifiable measures of performance and help track progress towards goals. These metrics are often tied to key performance indicators (KPIs) that reflect business priorities and customer expectations.
During six sigma black belt training, individuals learn to craft well-defined problems statements and define measurable objectives. This involves breaking down complex issues into manageable components, understanding root causes, and leveraging lean six sigma principles to identify and eliminate waste. The six sigma certification process ensures professionals have the tools to set clear goals, establish relevant metrics, and lay the groundwork for successful improvement initiatives.
Measure: Data Collection and Performance Analysis

In the Measure phase of the DMAIC process, organizations engaged in Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma initiatives focus on gathering relevant data and analyzing performance metrics to gain insights into their processes. This step is pivotal as it provides a factual basis for decision-making, ensuring that any subsequent improvements are guided by concrete evidence rather than assumptions. Data collection involves identifying key performance indicators (KPIs) specific to the project objectives and collecting both historical and real-time data using various tools and techniques. These may include statistical analysis, data mining, or even manual data extraction from records.
Once collected, the data is meticulously analyzed against established benchmarks and industry standards to assess current performance and identify variances or inefficiencies. This performance analysis allows for a deeper understanding of the process’s natural variability and any existing defects or causes of non-conformity. It also facilitates the identification of opportunities for improvement, setting the stage for the Analyze phase where these potential enhancements are evaluated systematically using robust statistical tools, with a goal to implement effective solutions that lead to sustained process enhancement and increased customer satisfaction, in line with Six Sigma certification requirements and Lean Six Sigma principles.
Improve & Control: Implementing Changes and Sustaining Results